Provide you with the latest enterprise and industry news.
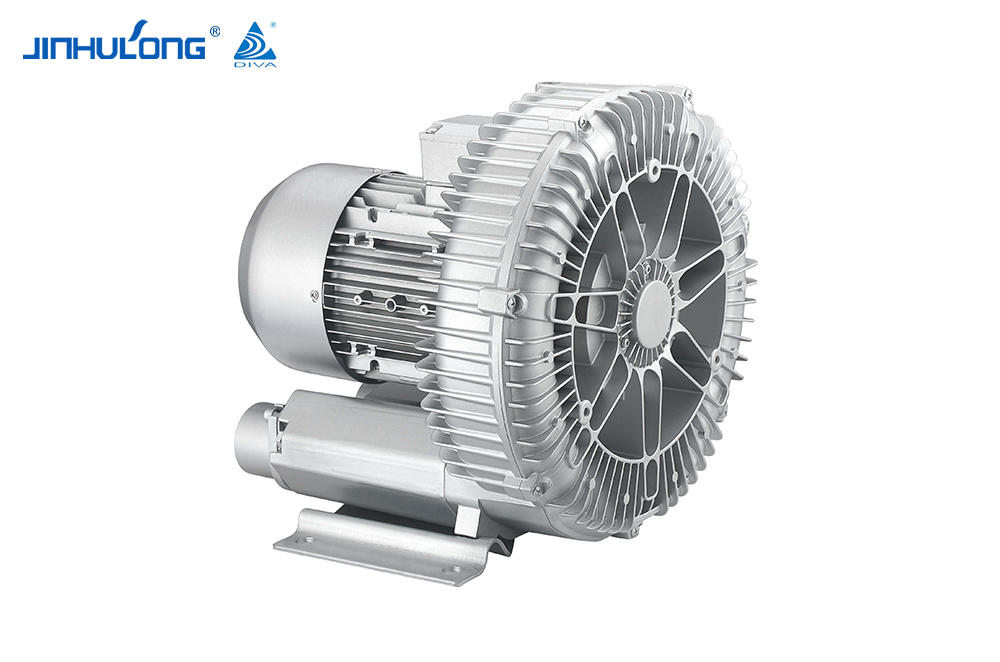
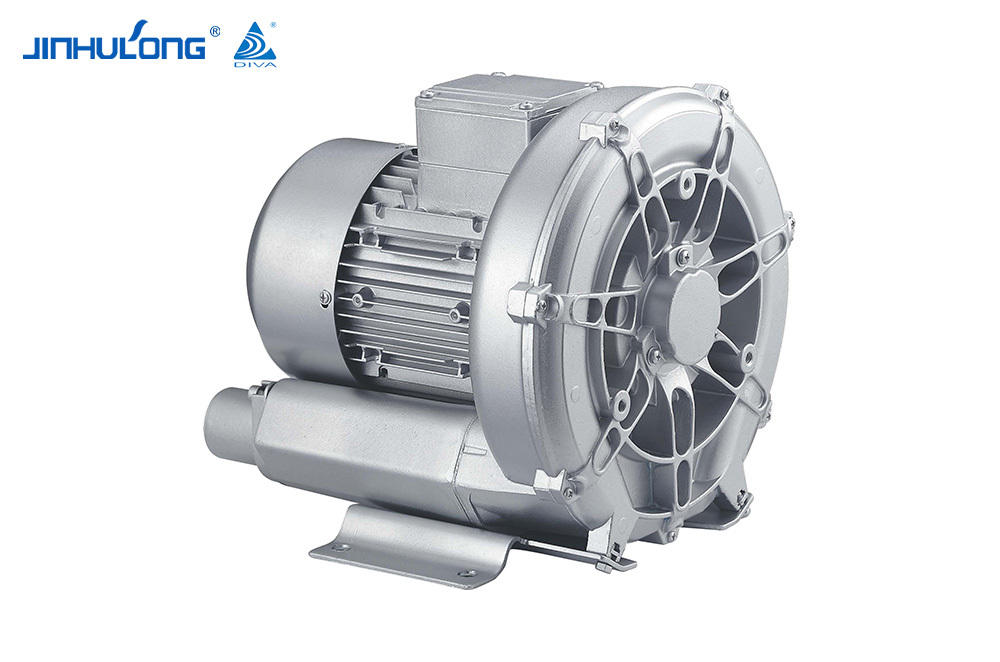
Design Custom Circumferential Aeration Aerator Manufacturer
In the intricate ecosystem of wastewater treatment, the role of aeration is paramount in sustaining the biological processes. The Circumferential Aeration Aerator, an essential component of many aeration systems, has a profound influence on the microbial community structure within the treatment tanks. This article delves into the effects of the Circumferential Aeration Aerator on microbial ecology and how it shapes the overall efficiency of the wastewater treatment process.

The Circumferential Aeration Aerator operates by providing a continuous flow of oxygen-rich air around the circumference of the aeration tank, ensuring a uniform distribution of oxygen. This uniformity is crucial for maintaining a balanced microbial community, as different microorganisms have varying oxygen demands. The aeration process not only supports the growth of aerobic bacteria, which are essential for breaking down organic matter but also influences the presence and activity of other microbial groups, such as anaerobic bacteria and facultative bacteria.
The impact of the Circumferential Aeration Aerator on microbial community structure is multifaceted. The Circumferential Aeration Aerator's design allows for a more even distribution of oxygen, which can cause a more diverse microbial population. This diversity is beneficial for the overall resilience of the treatment system, as it can withstand fluctuations in influent quality and environmental conditions. The Circumferential Aeration Aerator's ability to provide consistent oxygen levels fosters a stable environment for microorganisms, which in turn enhances the metabolic processes that degrade pollutants.
Secondly, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator can influence the selection pressure on microbial populations. By controlling the oxygen levels, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator can favor the growth of specific species that are better adapted to the prevailing conditions. This can cause the dominance of certain microbial groups that are more efficient at breaking down particular contaminants, thereby improving the treatment efficiency for specific pollutants.
Thirdly, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator's operation can also affect the physical structure of the microbial biofilms within the treatment tanks. The Circumferential Aeration Aerator's action can cause the formation of a more homogenous biofilm, which can enhance the transfer of nutrients and waste products between the microorganisms and their environment. This can cause a more efficient use of resources and a more effective breakdown of pollutants.
However, the influence of the Circumferential Aeration Aerator on microbial community structure is not without its challenges. Over-aeration can cause a decrease in the diversity of the microbial community, as less competitive species may be outcompeted by those that can tolerate higher oxygen levels. Additionally, under-aeration can cause the growth of anaerobic populations, which can produce undesirable by-products and reduce treatment efficiency.
In conclusion, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator plays a critical role in shaping the microbial community structure within wastewater treatment systems. By understanding the complex interactions between the Circumferential Aeration Aerator and the microbial ecology, treatment plant operators can optimize the aeration process to achieve more efficient and effective treatment outcomes. The Circumferential Aeration Aerator's impact on microbial community structure is a dynamic and complex phenomenon that warrants ongoing research and careful management to ensure the sustainability and success of wastewater treatment processes.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español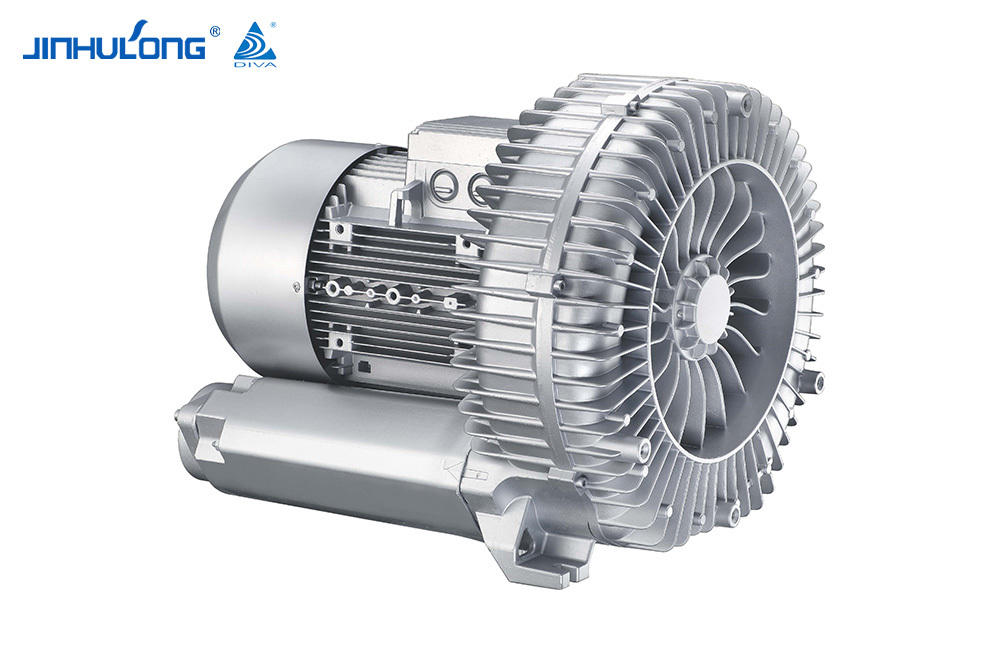





 0086-576-84893666
0086-576-84893666  0086-15757686666
0086-15757686666 
 Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang
Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang 
