Provide you with the latest enterprise and industry news.
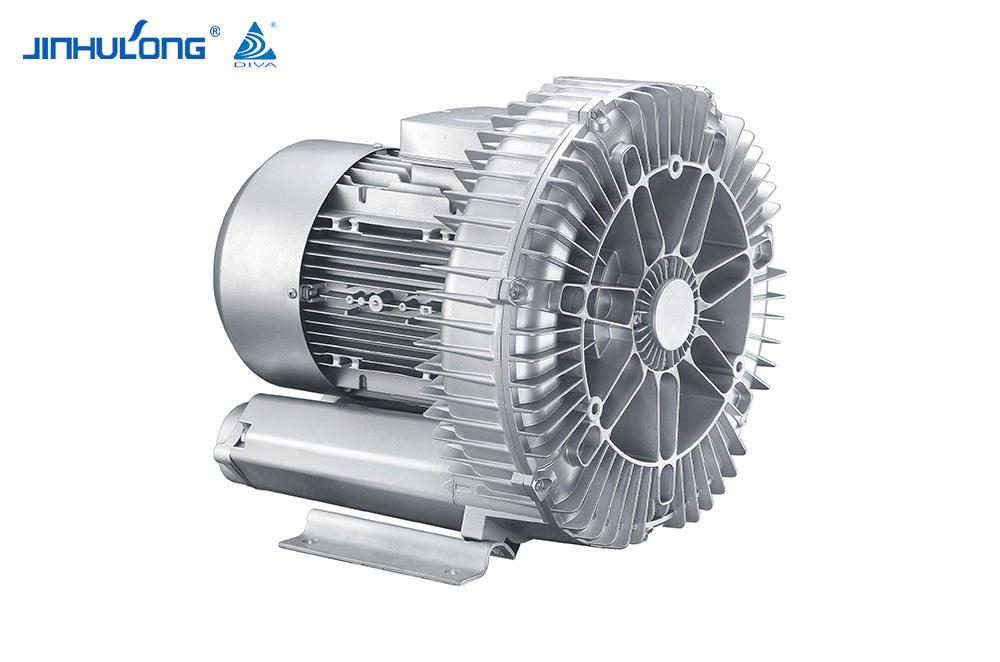
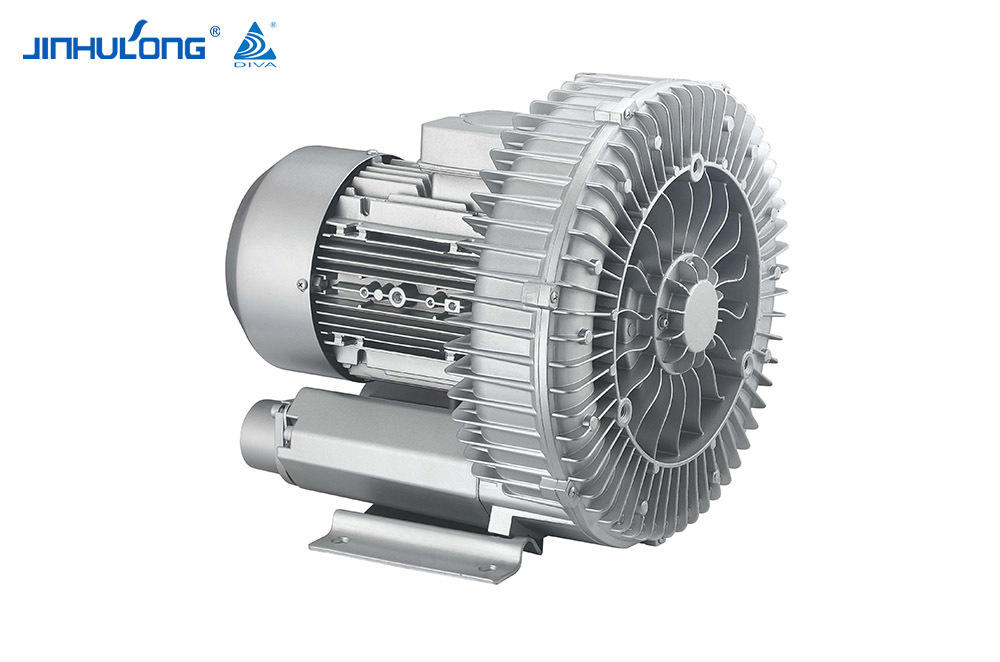
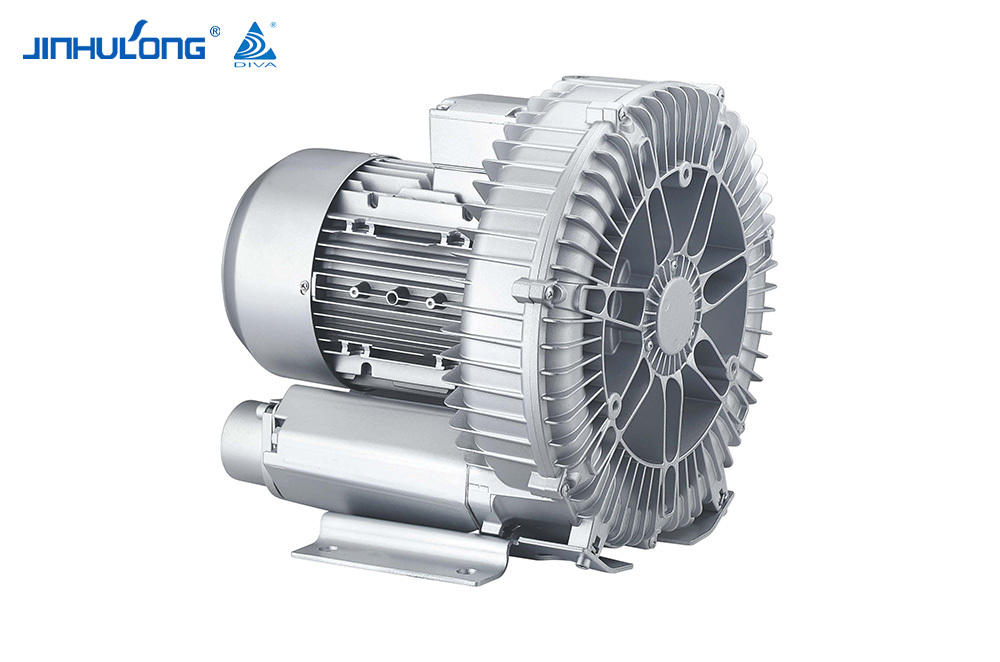
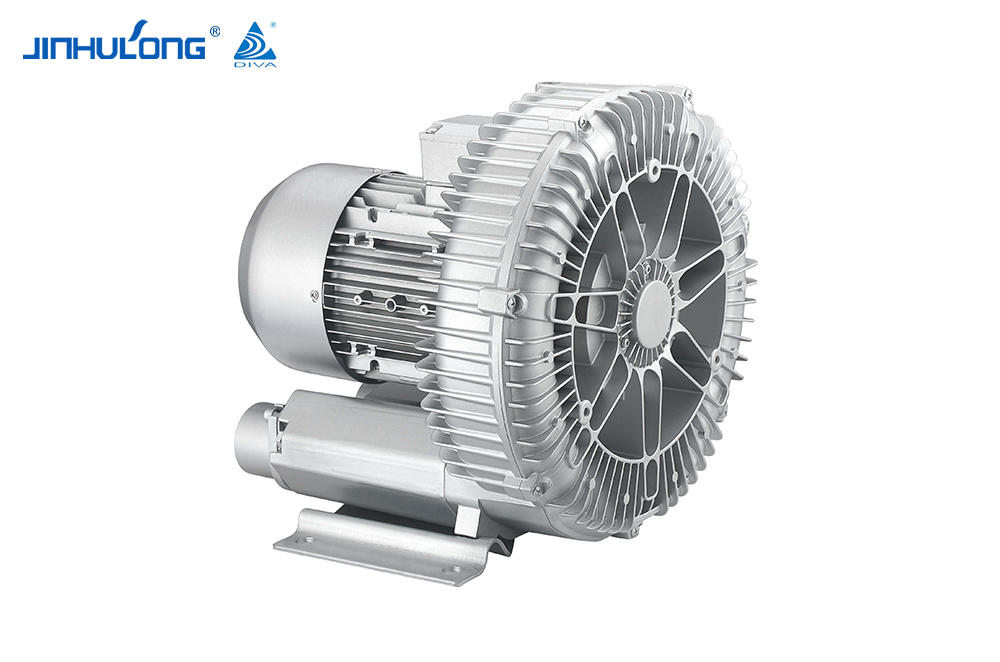
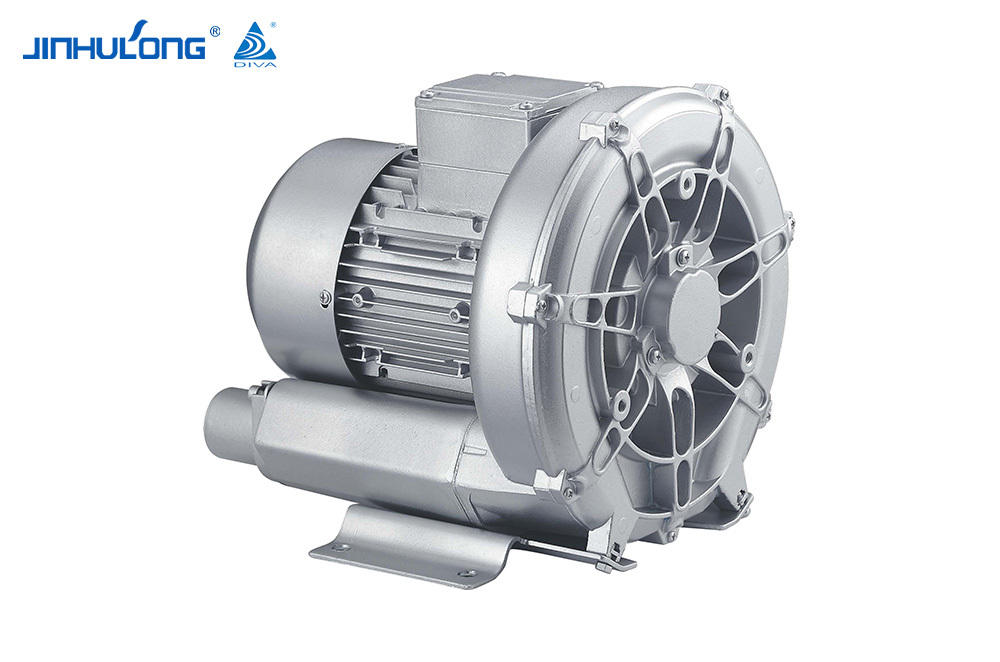
Sale Circumferential Aeration Aerator Exporter in China
As the temperatures dip during the winter months, the performance of aeration systems in wastewater treatment plants becomes a critical concern. The Circumferential Aeration Aerator, a prevalent technology in aeration systems, is no exception. This article seeks to evaluate the operational effectiveness of the Circumferential Aeration Aerator under the challenging conditions of low winter temperatures.

The Circumferential Aeration Aerator, known for its efficient oxygen transfer and distribution, faces unique challenges in colder climates. The reduced water temperature can affect the viscosity and density of water, altering the efficiency of the aeration process. Consequently, the oxygen transfer rate, which is crucial for the survival and activity of the microbial communities in the treatment process, can be significantly impacted.
In winter, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator's performance is tested as it must maintain the necessary oxygen levels to support the biological processes in the wastewater. The aerator's design, which typically involves a circular arrangement of aeration diffusers, is meant to create a uniform distribution of oxygen throughout the treatment tank. However, in low temperatures, the efficiency of this distribution may be compromised due to the increased resistance of water to the movement of air bubbles.
The Circumferential Aeration Aerator's ability to overcome these challenges is dependent on its construction and the materials used. Some aerators are made from materials that can withstand the physical stress of cold temperatures without significant degradation, ensuring that the aerator remains operational throughout the winter. However, not all aerators are created equal, and some may suffer from reduced efficiency or even mechanical failure in bad cold.
To counteract the effects of low temperatures, some treatment plants may opt to increase the power output of the Circumferential Aeration Aerator to maintain the same level of oxygen transfer. This, however, can cause increased energy consumption, which is a concern for both operational costs and environmental impact. Therefore, it is crucial to find a balance between maintaining the necessary oxygen levels and reducing energy expenditure.
Another factor to consider is the impact of low temperatures on the microbial community, which is directly influenced by the performance of the Circumferential Aeration Aerator. In colder conditions, the metabolic rates of these microorganisms slow down, which can affect the overall treatment efficiency. The aerator must provide sufficient oxygen to support these microbes even as their demand for oxygen decreases.
Researchers and engineers are continually developing strategies to improve the Circumferential Aeration Aerator's performance in winter conditions. This includes the use of heat exchangers to pre-warm the air before it is introduced to the aerator, as well as the development of more robust materials that can maintain their integrity in cold environments.
In conclusion, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator's performance in winter's low-temperature environment is a multifaceted issue that requires a comprehensive understanding of the physical and biological processes at play. By considering the effects of temperature on the aerator's efficiency, the viscosity of the water, and the metabolic rates of the microbial community, operators can better manage their treatment processes to ensure suitable performance throughout the year. The ongoing research and development in this area promise to bring about innovations that will further enhance the resilience and efficiency of the Circumferential Aeration Aerator in the face of winter's harsh conditions.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español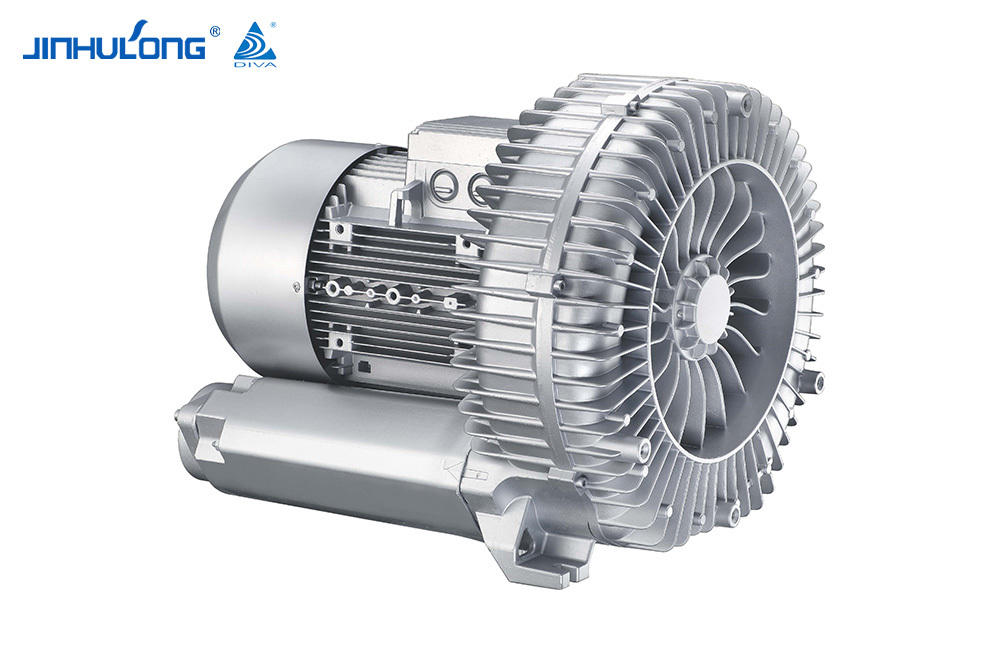





 0086-576-84893666
0086-576-84893666  0086-15757686666
0086-15757686666 
 Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang
Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang 
