Provide you with the latest enterprise and industry news.
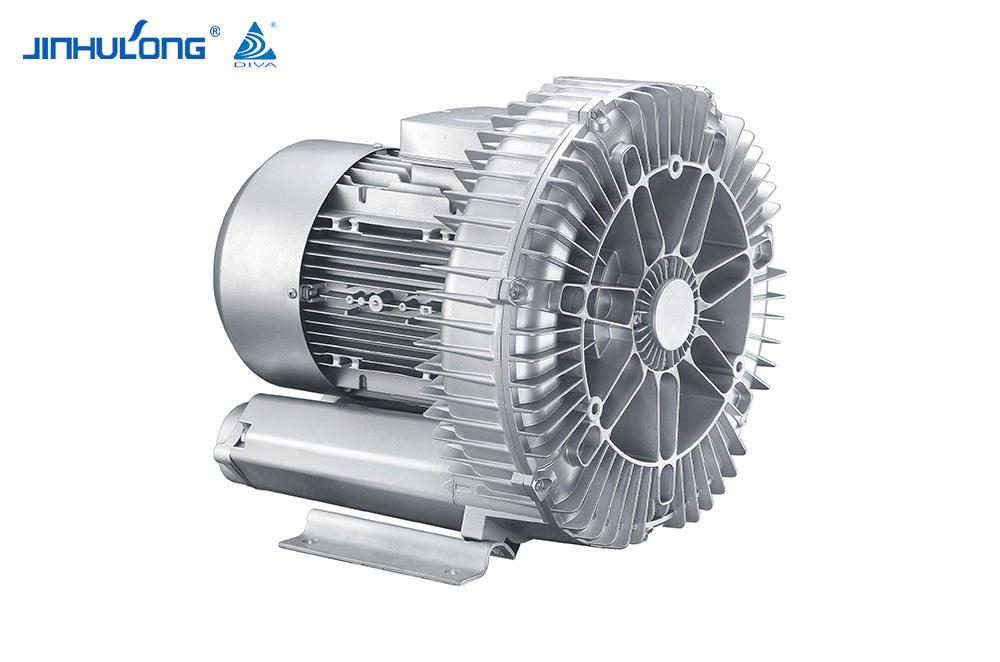
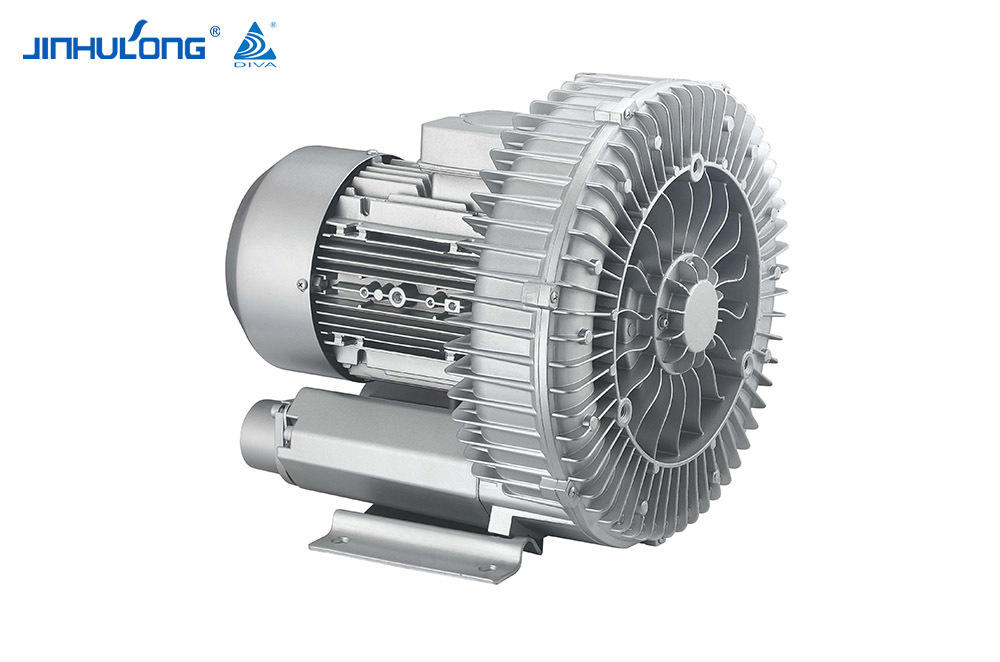
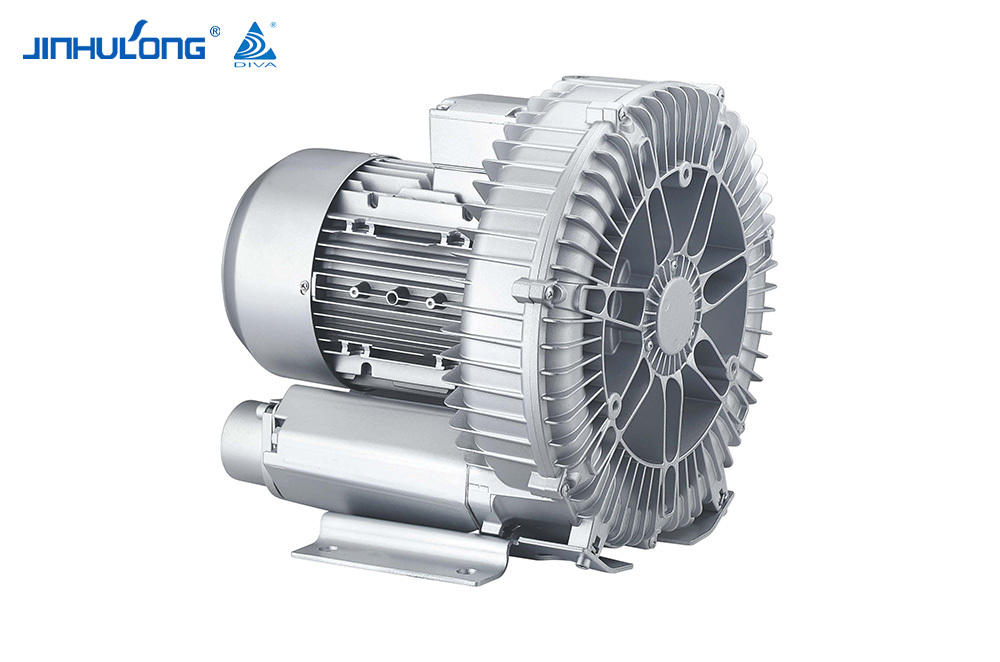
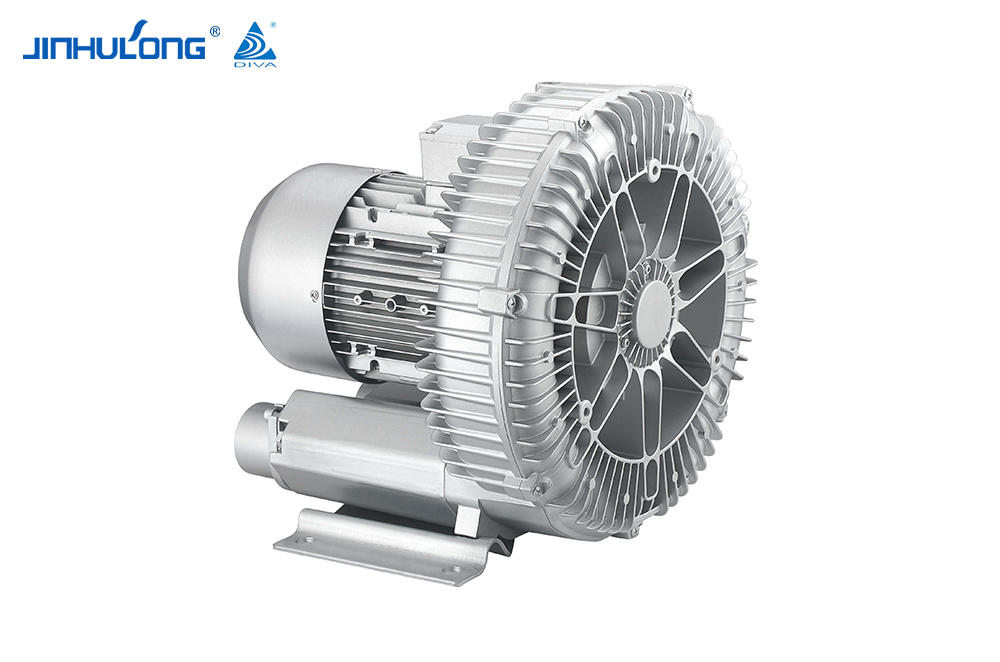
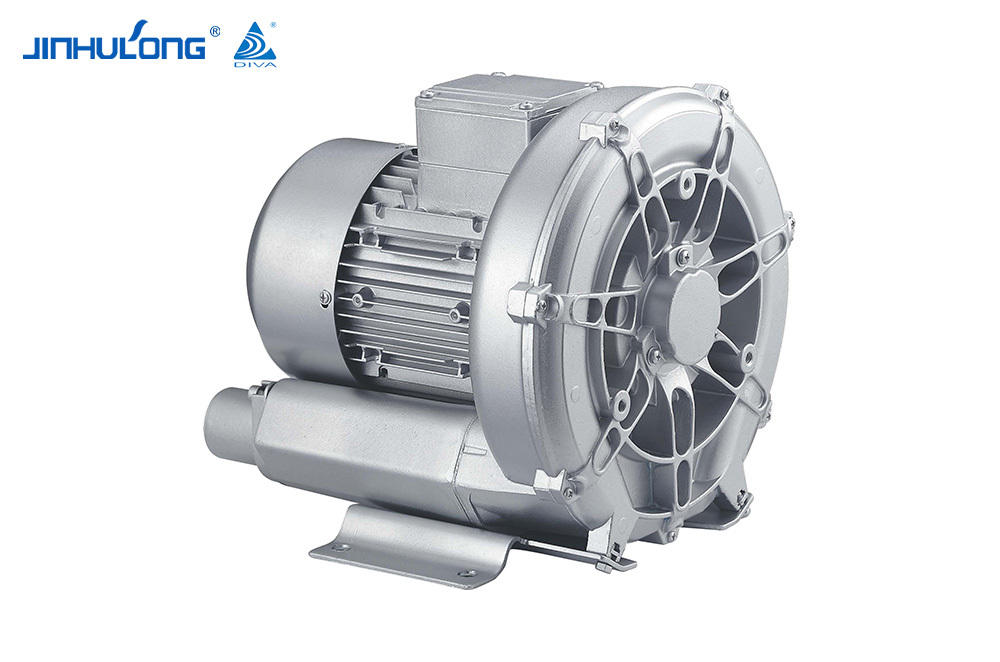
An aerator is a machine that is often used in fish farming. Its main function is to increase the oxygen level in the water to ensure that the fish in the water are not deprived of oxygen. At the same time, it can also inhibit the growth of anaerobic bacteria in the water, preventing the deterioration of pond water quality and threatening the living environment of fish. The aerator usually relies on its own air pump to pump air into the water in order to increase the oxygen content in the water.
The fish pond aerator is turned on in the early morning of a cloudy day: at this time, due to the weak sunlight intensity, the photosynthesis of phytoplankton produces less oxygen, and the dissolved oxygen condition of the entire water body is very poor. Therefore, starting in the morning, when the dissolved oxygen point is low, can address the risk of floating fish heads due to lack of oxygen around dawn.
The main performance indicators of aerators are specified as aeration volume and power efficiency. Aeration capacity refers to the amount of oxygen added to the water body by the aerator per hour, in kg/hour; power efficiency refers to the amount of oxygen consumed by the aerator to consume 1 kWh of electrical energy, in kg/hour kWh.
The fish pond aerator is turned on at noon on a sunny day: at this time, the temperature of the upper and lower water layers of the fish pond is very different, and the oxygen in the lower water cannot be replenished in time. If the aerator is turned on, the water resistance is destroyed and the upper and lower water layers can be interchanged. The temperature difference and oxygen difference are also greatly reduced, and the oxygen in the lower water can be replenished.
An aerator is a device that drives working parts by power such as a diesel engine or an electric motor so that the "oxygen" in the air is quickly transferred into the aquaculture water body. It can comprehensively utilize the functions of physics, chemistry and biology, not only to solve the problem of pond culture. The problem of fish floating head caused by hypoxia can eliminate harmful gases, increase the activity capacity and primary productivity of fish ponds, promote water convection exchange, improve water quality conditions, and reduce feed coefficients, thereby increasing the stocking density, improving the feeding intensity of feeding objects, and greatly increasing the mu Yield, promote growth, and fully achieve the purpose of increasing breeding income.
The fish pond aerator is turned on in the middle of the night to keep raining: in this case, the intensity of sunlight is weaker than that of a cloudy day. Phytoplankton in fish ponds produce very little oxygen through photosynthesis, so it must be turned on at midnight to prevent fish ponds. Fish pond aerators not turned on on sunny evenings: avoid agitating bottom sludge to increase oxygen consumption. At this point, the photosynthesis of the phytoplankton in the fish pond should stop and oxygen cannot be supplied to the water. If it is turned on, the dissolved oxygen in the upper layer water will decrease and cannot be replenished, and the dissolved oxygen in the lower layer water will be quickly consumed. As a result, the rate of oxygen consumption will increase, and fish floating heads are more likely to appear the next day.
The fish pond aerator is not turned on when it is cloudy: to avoid damage to phytoplankton, and use low light for photosynthesis on the surface. In addition to mastering the principle of "three open and two closed", fish ponds also need to flexibly grasp the length of the start-up time according to changes in seasons, water quality and weather. The start-up time is short, the start-up time is long after fertilization, the start-up time without fertilization is short, the start-up time is long when the wind is strong, and the start-up time is short when the wind is strong.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español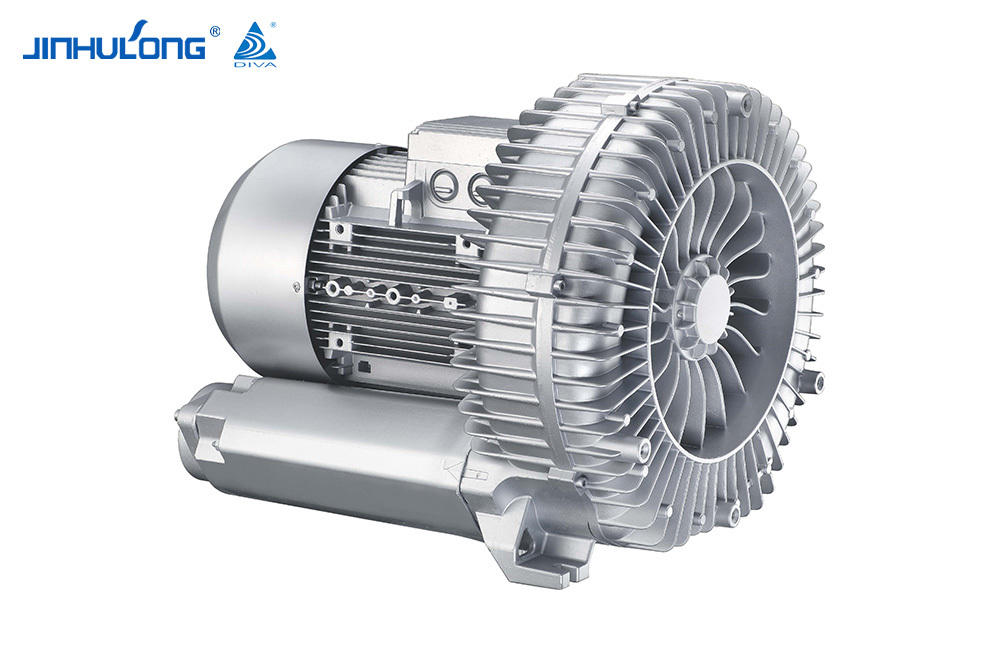





 0086-576-84893666
0086-576-84893666  0086-15757686666
0086-15757686666 
 Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang
Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang 
