Provide you with the latest enterprise and industry news.
Wholesale OEM Circumferential Aeration Aerator Producer
In the context of wastewater treatment, the selection of an aeration system is a critical decision that significantly impacts both the operational costs and the environmental footprint of the treatment process. The Circumferential Aeration Aerator, with its distinct design, has been a subject of interest for its potential energy efficiency. This article aims to provide a comprehensive comparison of the energy consumption of Circumferential Aeration Aerators with other aeration devices, examining their performance in various scenarios.

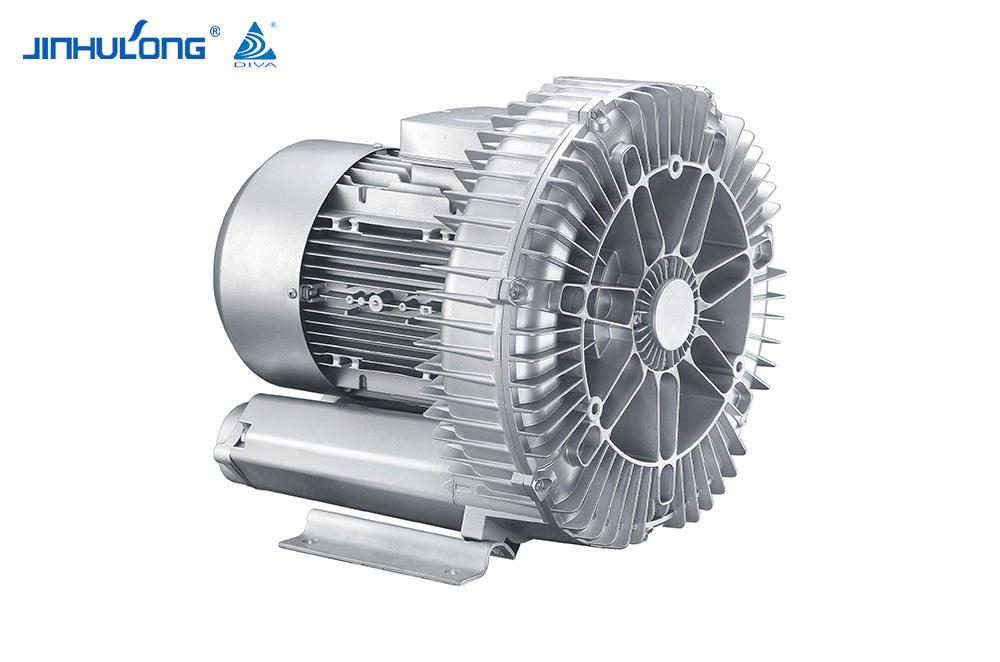
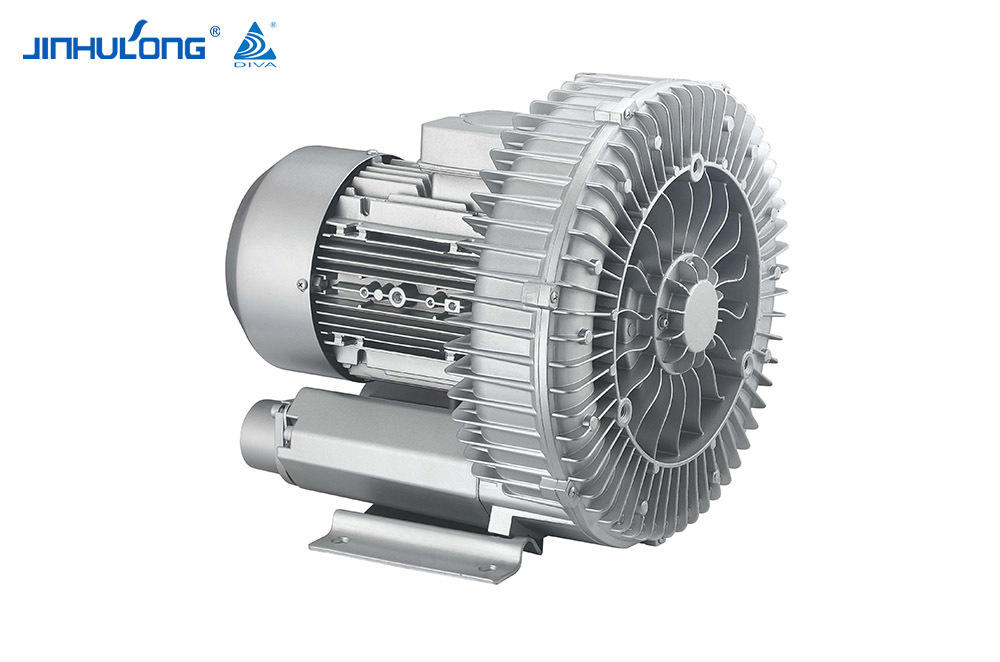
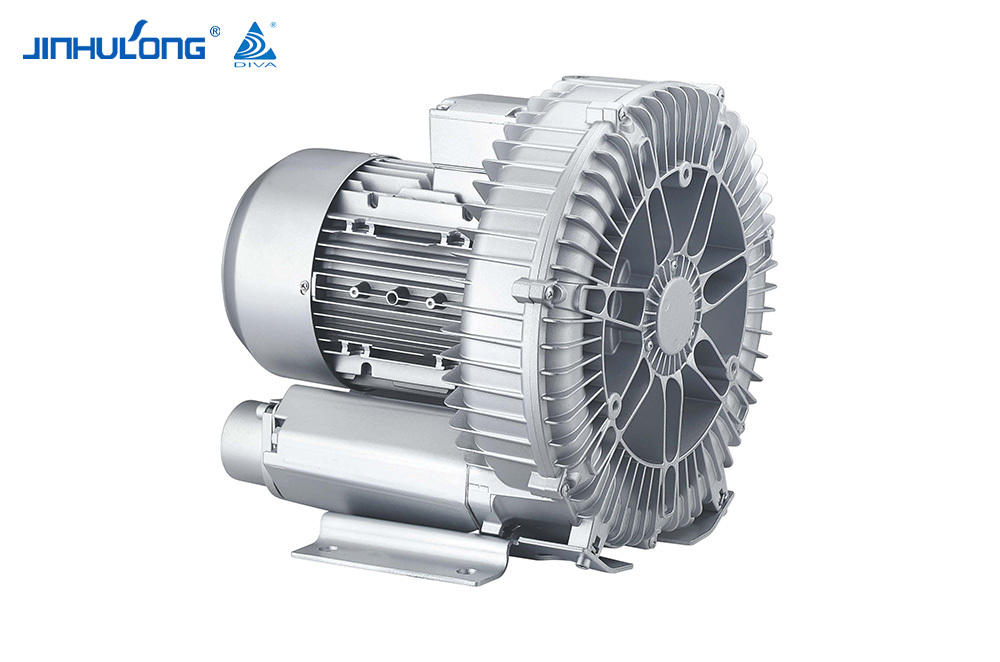
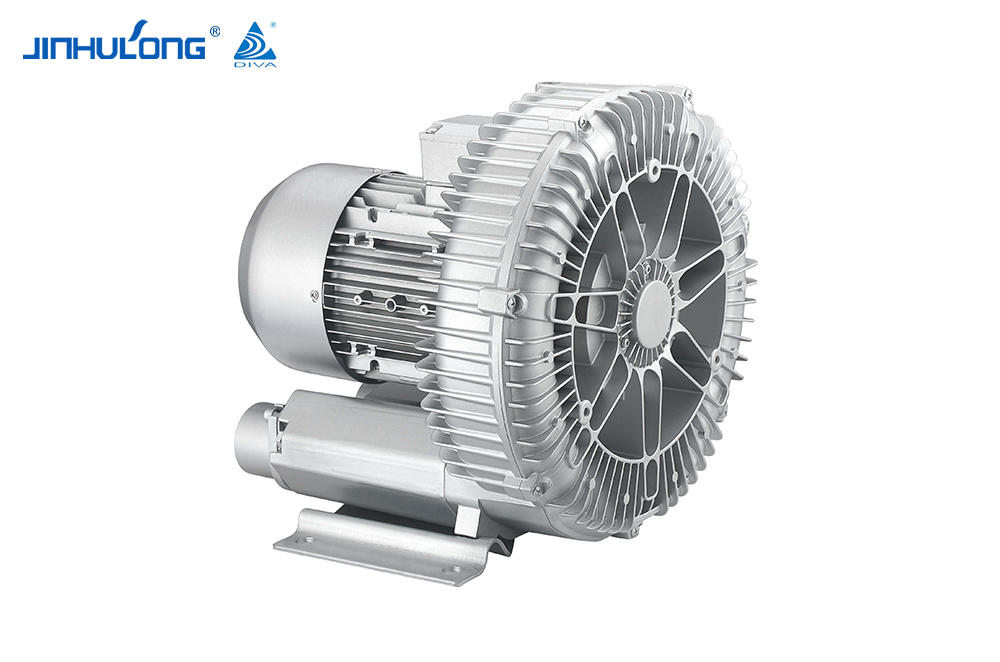
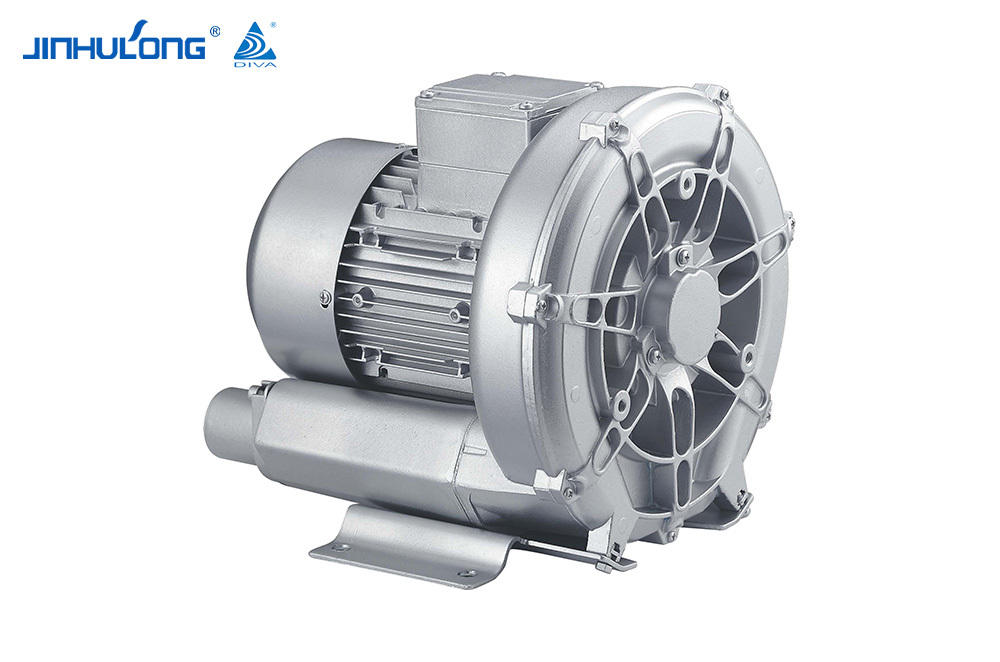
The Circumferential Aeration Aerator is a type of surface aerator that is designed to distribute air evenly across the entire cross-section of aeration basins, promoting efficient oxygen transfer and mixing. This design is intended to optimize the oxygenation process, which is essential for the aerobic decomposition of organic matter in wastewater. The energy consumption of such a system is a crucial factor in determining its overall efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
When comparing the energy consumption of a Circumferential Aeration Aerator with other aeration devices, such as fine bubble diffusers or mechanical surface aerators, several factors must be taken into account. These include the oxygen transfer efficiency, the power input per unit of oxygen transferred, and the operational conditions of the wastewater treatment plant.
The Circumferential Aeration Aerator, due to its even distribution of air, tends to have a higher oxygen transfer efficiency compared to some other aeration systems. This efficiency translates into lower energy consumption per unit of oxygen transferred, making it an attractive option for energy-sensitive applications. Studies have shown that the Circumferential Aeration Aerator can achieve oxygen transfer efficiencies that are competitive with, and in some cases good to, those of fine bubble diffusers, which are known for their high efficiency but can be more energy-intensive.
However, the energy consumption of the Circumferential Aeration Aerator is not solely determined by its oxygen transfer efficiency. The power input required to operate the system is also a significant factor. The Circumferential Aeration Aerator, being a mechanical system, requires less power per unit of oxygen transferred compared to some other mechanical aerators. This is due to its design, which allows for a more direct and efficient use of energy to move air into the wastewater.
In terms of operational conditions, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator can be more versatile than other systems. It can be easily adjusted to accommodate changes in the volume of wastewater or the required oxygen levels, which can cause further energy savings. This adaptability is particularly important in treatment plants that experience fluctuating influent loads or seasonal variations in oxygen demand.
Despite these advantages, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator is not without its challenges. Maintenance costs and the need for regular inspection to ensure the integrity of the aeration system can add to the operational expenses. However, with proper maintenance and management, these costs can be reduced, and the long-term energy savings can make the Circumferential Aeration Aerator a more economical choice.
In conclusion, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator offers a competitive energy consumption profile when compared to other aeration devices. Its high oxygen transfer efficiency, lower power input requirements, and adaptability to varying operational conditions make it a strong contender for wastewater treatment plants seeking to optimize their energy usage. As environmental concerns and energy costs continue to rise, the Circumferential Aeration Aerator's energy efficiency becomes an increasingly important consideration in the selection of aeration technologies for wastewater treatment.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español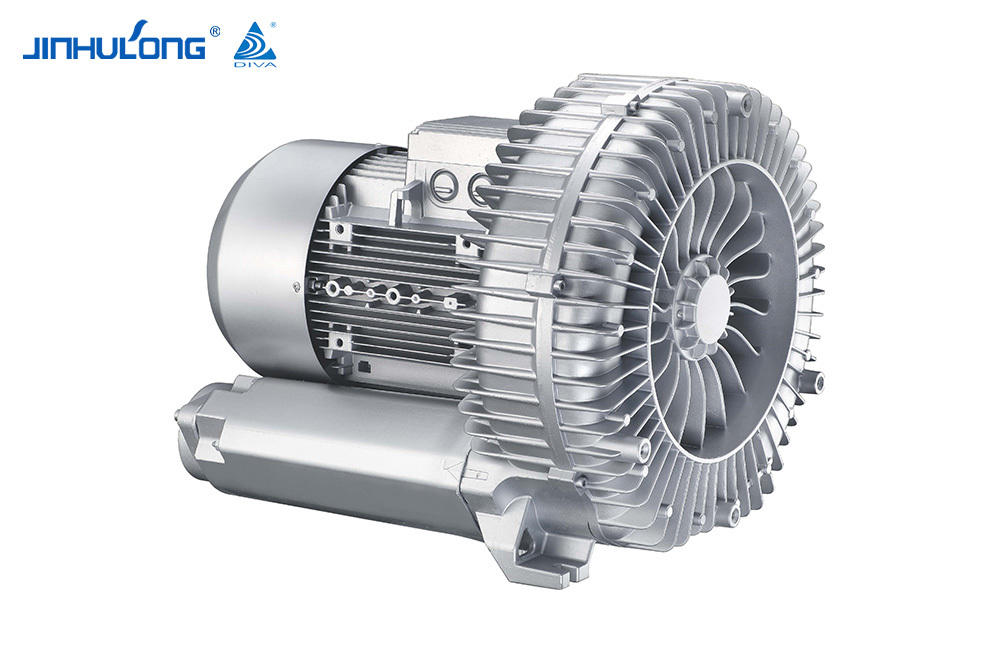





 0086-576-84893666
0086-576-84893666  0086-15757686666
0086-15757686666 
 Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang
Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang 
