Provide you with the latest enterprise and industry news.
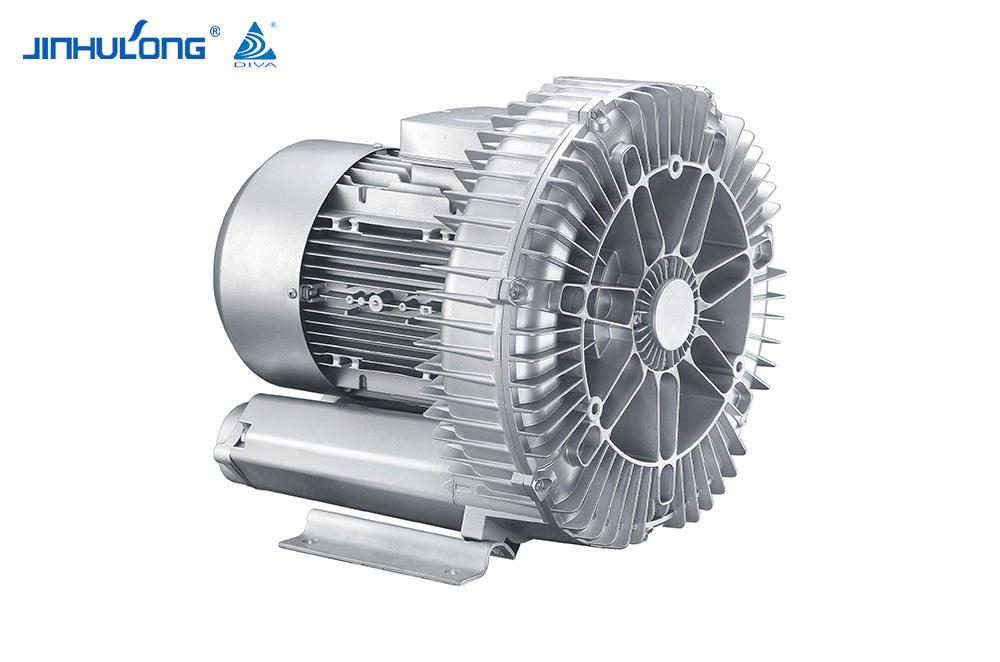
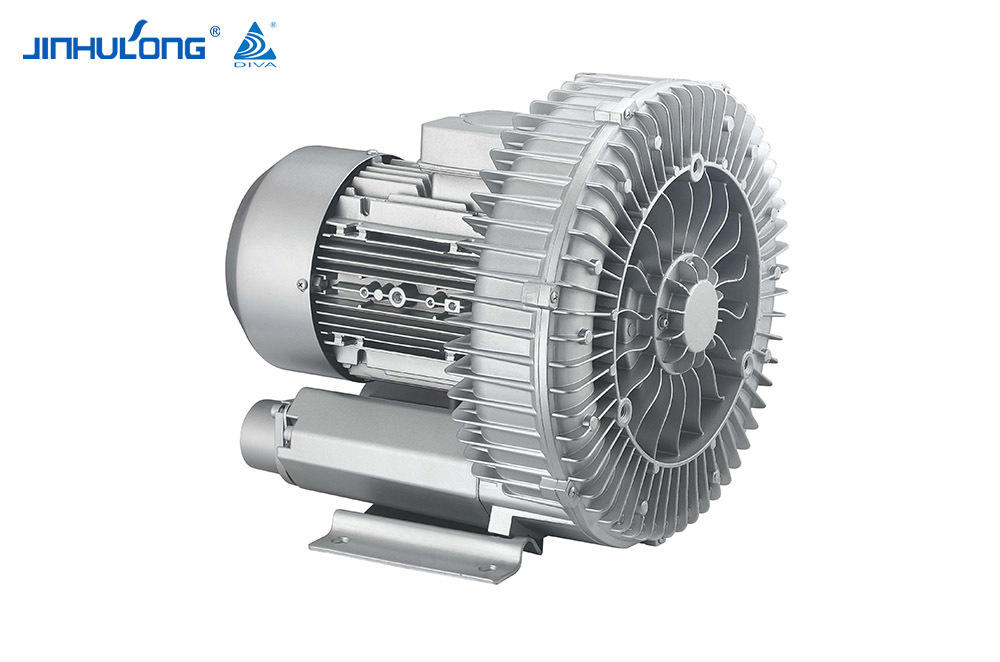
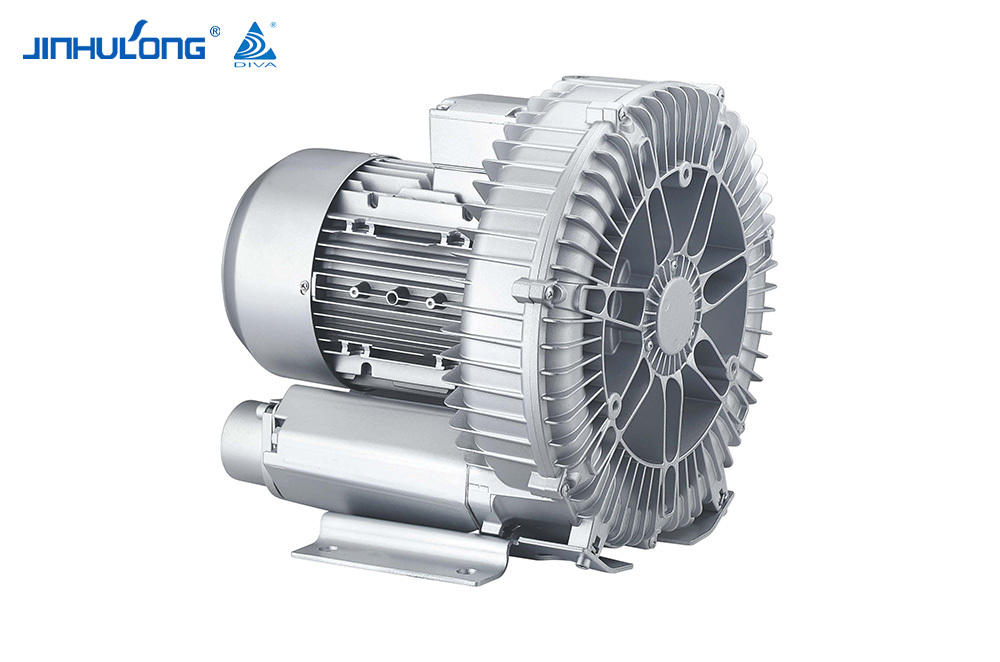
Custom High Quality Impeller Aerator Wholesaler in China
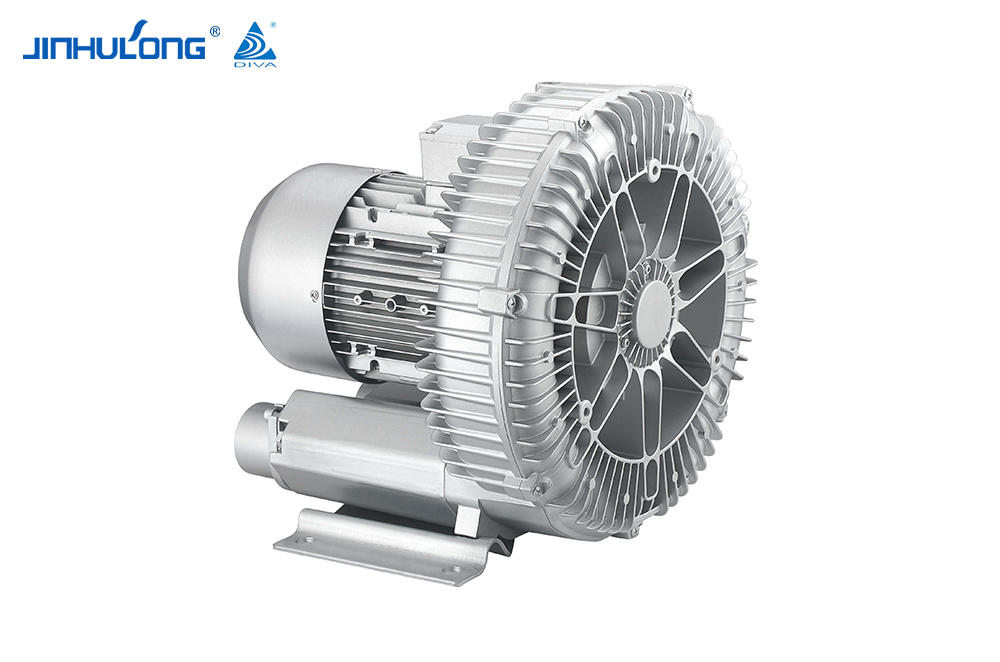
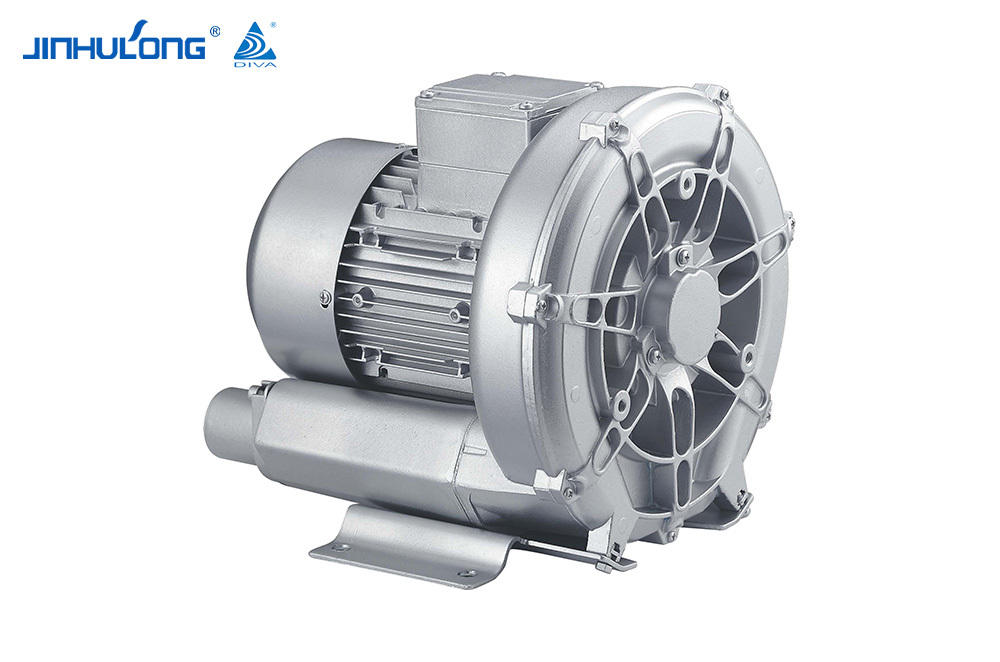
In the realm of water aeration, Impeller Aerator is indispensable for its ability to oxygenate water bodies, a process that is essential for maintaining the health of aquatic ecosystems and the efficiency of wastewater treatment systems. While these devices serve a critical function, their operation is not without its drawbacks. One such drawback is the noise generated by Impeller Aerators, which can have significant implications for both the environment and the communities in proximity to these installations. This article aims to explore the noise levels associated with Impeller Aerators, the factors that contribute to these levels, and the strategies that can be employed to mitigate their acoustic impact.
The noise produced by Impeller Aerators is a result of the mechanical action of the impeller blades as they churn through the water, creating turbulence and air bubbles. This process generates sound waves that propagate through the air and water, causing audible noise levels that can be measured in decibels (dB). The intensity of the noise can vary widely depending on several factors, including the size and speed of the impeller, the design of the aerator, and the characteristics of the water being aerated.
One of the primary considerations in assessing the noise levels of Impeller Aerators is the frequency of the sound waves produced. Impeller Aerators typically generate a range of frequencies, with some devices producing more low-frequency noise and others generating higher-frequency sounds. The human ear is more sensitive to certain frequencies, and the perception of noise can be influenced by the presence of these frequencies in the sound spectrum of the Impeller Aerator.
The speed at which the impeller rotates is another critical factor that affects the noise levels of Impeller Aerators. Higher rotational speeds generally result in increased noise levels, as the impeller blades interact with the water more rapidly, creating more turbulence and air bubbles. However, the relationship between speed and noise is not always linear, and other factors such as impeller design and water conditions can also play a role.
The design of the Impeller Aerator itself can have a significant impact on the noise levels it generates. Some designs incorporate features that are intended to reduce noise, such as the use of quieter impeller blades or the incorporation of sound-absorbing materials. Additionally, the overall construction and materials used in the aerator can influence its acoustic properties, with some materials being more conducive to noise reduction than others.
The characteristics of the water being aerated can also influence the noise levels produced by Impeller Aerators. Factors such as water temperature, salinity, and the presence of suspended particles can all affect how sound waves propagate through the water, potentially altering the perceived noise levels. Moreover, the depth and volume of the water body can also play a role in the transmission of noise, with larger and deeper bodies potentially attenuating the sound to some extent.
In conclusion, the noise levels of Impeller Aerators are a complex issue that is influenced by a variety of factors, including the design of the device, the speed of operation, and the characteristics of the water being aerated. By understanding these factors and implementing strategies for noise mitigation, it is possible to reduce the acoustic impact of Impeller Aerators while still benefiting from their essential function in water aeration. This approach not only supports the sustainability of aquatic ecosystems and wastewater treatment processes but also contributes to the well-being of the communities and environments in which these devices are used.


 中文简体
中文简体 English
English Español
Español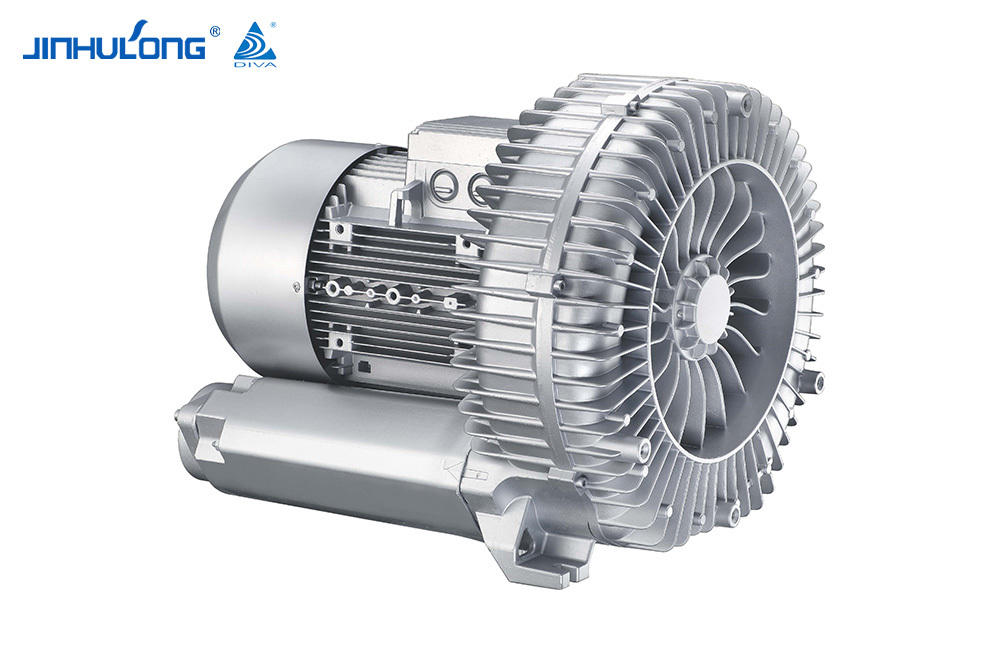





 0086-576-84893666
0086-576-84893666  0086-15757686666
0086-15757686666 
 Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang
Tangshan Chen, Shabu Town, Huangyan, Taizhou, Zhejiang 
